
Which Automation Tool Reigns Supreme? RPA vs. BPA
Why Understanding BPA and RPA Matters for Your Business Growth
BPA and RPA represent two powerful automation approaches that can transform how your business operates, but they serve very different purposes. Understanding the distinction is crucial for making the right investment in your company's future.
Quick Answer: BPA vs RPA
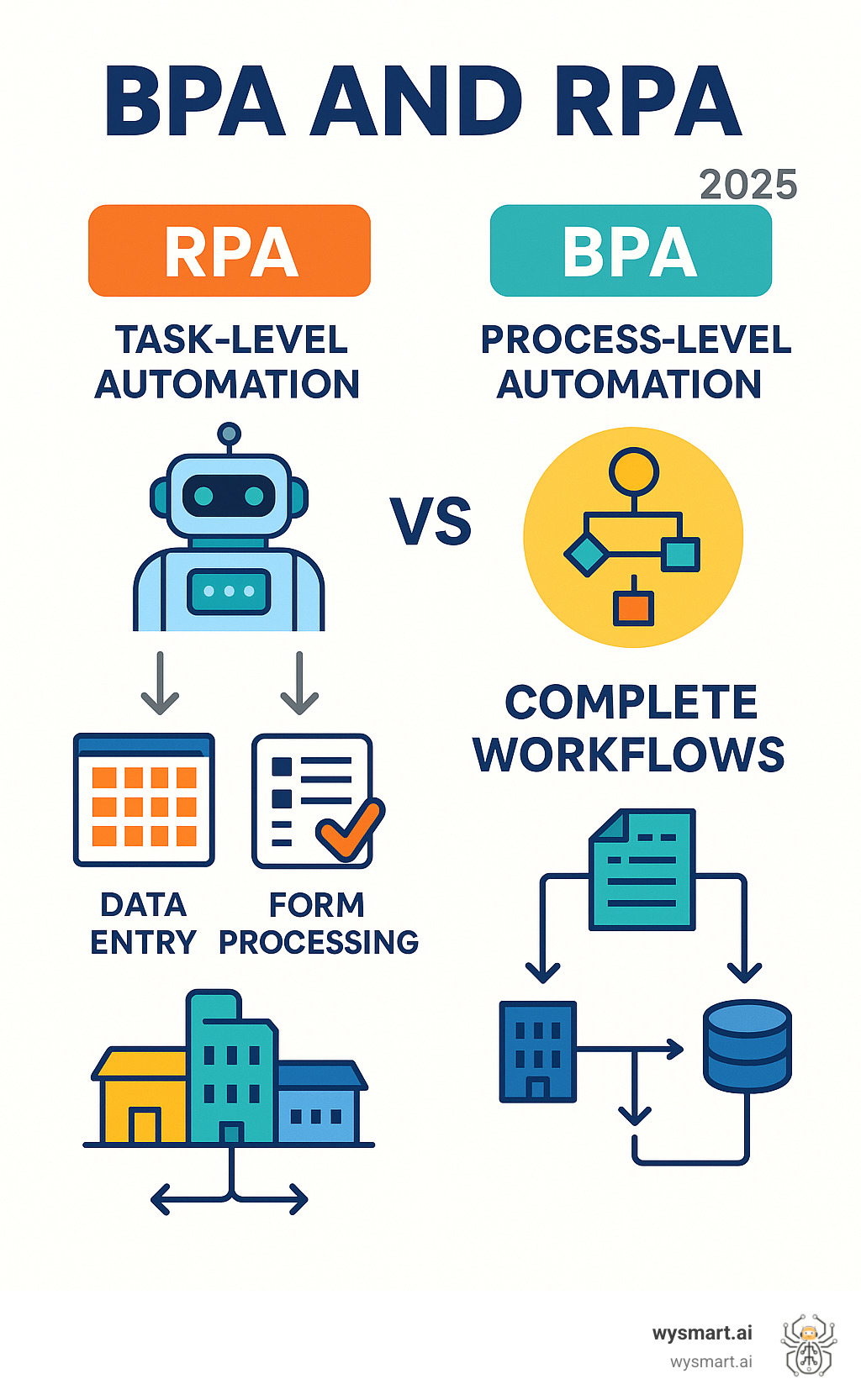
RPA (Robotic Process Automation): Automates individual, repetitive tasks using software bots
BPA (Business Process Automation): Optimizes entire workflows and processes end-to-end
Key Difference: RPA handles specific tasks; BPA redesigns complete business processes
Best Use: RPA for quick wins on routine work; BPA for strategic process improvement
The global process automation market has surged to $202.54 billion as of 2024, driven by businesses seeking to eliminate inefficiencies and boost productivity. Small business owners face mounting pressure to do more with less - juggling customer acquisition, managing operations, and trying to compete with larger companies that have dedicated automation teams.
Many business owners get stuck choosing between these technologies without understanding what each actually does. RPA excels at mimicking human actions for repetitive tasks like data entry or invoice processing. BPA takes a bigger-picture approach, redesigning entire workflows to eliminate bottlenecks and connect different systems.
The confusion is understandable. Both promise to save time and reduce errors, but they work at completely different levels of your business operations. Making the wrong choice can lead to wasted resources, frustrated employees, and minimal impact on your bottom line. However, understanding these technologies opens up opportunities for significant competitive advantages.
Consider this: while your competitors are still manually processing invoices or struggling with disconnected systems, you could be leveraging automation to serve customers faster, reduce operational costs, and scale your business more effectively. The businesses that accept the right automation strategy today will be the ones that dominate their markets tomorrow.
I'm Joey Martin, and through my work helping small businesses implement AI-powered solutions at WySmart.ai, I've seen how the right automation choice can make or break a company's efficiency goals. My experience working with hundreds of local business owners has taught me that understanding BPA and RPA is essential for making smart automation investments that actually move the needle.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Think of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as a digital assistant that works 24/7 without errors. RPA uses software robots, or "bots," to mimic human actions on a computer. These bots interact with applications at the user interface (UI) level—clicking, typing, and navigating—to execute repetitive, rules-based tasks with speed and precision.
RPA is ideal for automating processes that use structured data, such as information in spreadsheets or standard forms. If you can map out the steps of a task, an RPA bot can likely perform it. The technology works by recording human actions and then replicating them exactly, making it particularly effective for tasks that follow predictable patterns.
What makes RPA particularly appealing to small businesses is its non-invasive nature. Unlike other automation solutions that require significant changes to existing systems, RPA bots work on top of your current applications. This means you can start automating without expensive system overhauls or lengthy IT projects.
Core Functionalities and Common Use Cases for RPA
RPA is best for high-volume, mundane tasks that don't require complex decision-making. This frees up your team for more strategic work. The technology excels in environments where accuracy and consistency are paramount, delivering results that often exceed human performance in terms of speed and error rates.
Common use cases include:
Data entry and migration: Bots move information between systems with perfect accuracy, which is especially useful for legacy systems without modern APIs. They can work continuously without fatigue, processing thousands of records in the time it would take a human to handle dozens.
Invoice processing: Bots can extract invoice data, validate it against purchase orders, and initiate payment processes. This reduces processing time from days to hours while eliminating costly human errors.
Report generation: Bots automatically gather data from various sources and compile it into reports. They can generate daily, weekly, or monthly reports without human intervention, ensuring stakeholders always have up-to-date information.
Customer service routing: Bots handle initial customer inquiries, collect details, and route them to the appropriate human agent. This improves response times and ensures customers reach the right department immediately.
Reconciling transactions: Bots match transactions from different financial systems and flag discrepancies for review. This critical function helps maintain financial accuracy while reducing the time spent on manual reconciliation.
By automating these tasks, RPA delivers immediate improvements in speed and accuracy, reduces human error, and allows your employees to focus on creative, high-value activities that grow your business. The return on investment is often visible within weeks of implementation, making RPA an attractive option for businesses seeking quick efficiency gains.
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)?
While RPA automates individual tasks, Business Process Automation (BPA) is the master architect of your entire operation. BPA focuses on redesigning and optimizing complete, end-to-end workflows that span multiple departments and systems.
Instead of just making one step faster, BPA takes a holistic view to eliminate bottlenecks and improve collaboration. Where RPA works on the surface of applications, BPA integrates deeply with your core business systems using APIs, ensuring a seamless flow of information. Think of it this way: if RPA automates a single step in a recipe, BPA redesigns the entire kitchen for maximum efficiency.
Core Functionalities and Common Use Cases for BPA
BPA is a strategic investment designed to achieve broad organizational goals like enhancing customer experience and cutting operational costs. Its power lies in process modeling and orchestration, allowing you to map, coordinate, and manage complex workflows. Key functionalities include deep system integration to eliminate data silos and sophisticated rules engines to handle complex decisions and exceptions.
Common use cases for BPA include:
Employee onboarding: Automating the entire process from offer letter to system access and training schedules for a smooth new-hire experience.
Procurement and purchasing: Streamlining purchase order approvals, vendor management, and invoice processing.
Customer lifecycle management: Optimizing the entire customer journey, from initial contact to ongoing support, for a consistent experience.
Loan approvals: Automating complex approval chains that involve credit checks, documentation verification, and routing across multiple systems.
The result is dramatically improved efficiency, fewer errors, and scalable operations that support business growth.
Choosing Your Automation Path: Key Considerations for BPA and RPA
The right automation choice isn't about which technology is better, but which one fits your specific business challenge. BPA and RPA solve different problems: RPA offers quick, tactical wins on individual tasks, while BPA provides strategic, long-term change of entire workflows.
Here's a direct comparison:
Feature Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Business Process Automation (BPA) Scope Task-level (micro) Process-level (macro) Integration UI-level (mimics human actions) API-level (deep system connection) Complexity Simple, rules-based, structured data Complex, multi-step, variable data Deployment Faster, less costly, tactical wins Slower, larger investment, strategic change IT Involvement Minimal Significant
The growing importance of this decision is highlighted by a 2022 McKinsey survey, which found that automating business processes will account for 25% of industrial companies' spending over the next five years.
When to Choose RPA for Your Business
Opt for RPA to achieve quick wins and immediate efficiency gains. It's the ideal choice for:
High-volume, repetitive tasks: Automating things like data entry, form filling, and invoice processing.
Stable, unchanging processes: Works best when the steps are predictable and consistent.
Legacy systems without APIs: Bots can interact with older software at the UI level.
Limited IT resources: RPA can often be implemented by business users with minimal technical support.
Choose RPA when your goal is to improve individual task efficiency quickly and cost-effectively.
When to Choose BPA for Your Business
Select BPA when you need to overhaul how your business operates. It's the right solution for:
Complex, multi-step processes: Streamlining workflows that cross multiple departments and systems.
End-to-end workflow redesign: Reimagining an entire process for maximum efficiency, not just speeding up one part.
Integrating multiple systems: Connecting your CRM, ERP, and other platforms to eliminate data silos.
Processes with frequent changes: BPA is more flexible and can adapt to evolving business needs.
Choose BPA when you have strategic digital change goals and are ready to invest in long-term, scalable improvements.
Better Together: How RPA and BPA Create a Powerful Synergy
The most successful automation strategies don't force you to choose between BPA and RPA—they combine both technologies to create what experts call "hyperautomation." This approach leverages the strengths of each technology while compensating for their individual limitations.
RPA excels at executing specific tasks but can't optimize the overall process flow. BPA designs efficient workflows but needs tools to execute individual steps. Together, they create a comprehensive automation ecosystem that transforms both how work gets done and how efficiently it flows through your organization.
Consider a customer onboarding process: BPA redesigns the entire workflow to eliminate bottlenecks and ensure smooth handoffs between departments. Within that optimized process, RPA bots handle specific tasks like data entry, document verification, and system updates. The result is a seamless experience that's both strategically sound and tactically efficient.
Overcoming Individual Limitations
When used together, BPA and RPA address each other's weaknesses:
RPA's limitation: Can't see the bigger picture or optimize process flow
BPA's solution: Provides strategic process design and workflow orchestration
BPA's limitation: Requires tools to execute individual tasks within the optimized process
RPA's solution: Handles specific task automation with precision and speed
This synergy is particularly powerful for small businesses because it allows you to start with quick RPA wins while building toward comprehensive BPA change. You can automate high-impact tasks immediately, then gradually expand to full process optimization as your automation maturity grows.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between RPA and BPM?
While RPA is a technology that automates specific tasks, Business Process Management (BPM) is a discipline focused on analyzing, designing, and continuously improving business processes. BPM provides the strategic framework for understanding how work flows through your organization, while RPA serves as one of many tools that can execute tasks within that framework.
Think of BPM as the architect who designs the blueprint, and RPA as the construction worker who builds specific components. BPM identifies which processes need improvement and how they should be redesigned, while RPA automates the repetitive tasks within those improved processes.
How do DPA and BPA relate?
Digital Process Automation (DPA) represents the evolution of BPA, with a stronger focus on customer experience and end-to-end digital change. While BPA traditionally focused on internal process efficiency, DPA emphasizes creating seamless digital experiences that span both internal operations and customer interactions.
DPA typically leverages low-code platforms and modern integration technologies to create more agile, customer-centric processes. It's particularly relevant for businesses looking to digitize customer-facing processes like online ordering, support ticket management, or digital onboarding experiences.
Can RPA and BPA be used by small businesses?
Absolutely. Modern BPA and RPA solutions are increasingly designed with small businesses in mind. Low-code RPA platforms allow business users to create simple automations without extensive technical knowledge, while cloud-based BPA solutions offer enterprise-grade capabilities at small business prices.
The key is starting with high-impact, low-complexity processes. Focus on automating tasks that consume significant time or are prone to errors, then gradually expand your automation footprint as you gain experience and see results. Many small businesses see positive ROI within the first few months of implementation.
Implementation Best Practices for BPA and RPA Success
Starting Your Automation Journey
Successful automation implementation requires careful planning and realistic expectations. Begin by conducting a thorough audit of your current processes to identify the best candidates for automation. Look for processes that are high-volume, rule-based, and consume significant employee time.
For RPA implementation, start with processes that have:
Clear, documented steps
Minimal exceptions or variations
Structured data inputs
High frequency of execution
Low complexity decision-making
For BPA implementation, focus on processes that:
Span multiple departments or systems
Have frequent bottlenecks or delays
Require approvals or routing decisions
Impact customer experience significantly
Generate compliance or audit requirements
Common Implementation Pitfalls to Avoid
Many businesses make critical mistakes that undermine their automation success:
Over-automating too quickly: Start small and scale gradually. Attempting to automate everything at once often leads to project failures and employee resistance.
Ignoring change management: Employees need training and support to work effectively with automated processes. Invest in proper change management to ensure adoption.
Automating broken processes: Fix and optimize processes before automating them. Automation will only make bad processes fail faster.
Lack of governance: Establish clear guidelines for bot management, process ownership, and performance monitoring to prevent automation sprawl.
Measuring Success and ROI
Track key metrics to demonstrate the value of your automation investments:
Time savings: Measure hours saved per process and calculate the monetary value
Error reduction: Track accuracy improvements and associated cost savings
Employee satisfaction: Monitor how automation affects job satisfaction and retention
Customer experience: Measure improvements in response times and service quality
Scalability: Assess your ability to handle increased volume without proportional staff increases
The Future of Business Automation: Trends and Opportunities
Emerging Technologies Shaping Automation
The automation landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with artificial intelligence and machine learning enhancing both BPA and RPA capabilities. Intelligent automation combines traditional rule-based automation with AI-powered decision-making, enabling businesses to automate more complex processes that previously required human judgment.
Conversational AI is revolutionizing customer service automation, allowing businesses to handle sophisticated customer interactions through chatbots and virtual assistants. Computer vision enables bots to process unstructured documents and images, expanding automation possibilities beyond structured data.
Process mining technology helps businesses find automation opportunities by analyzing system logs and user interactions to identify inefficient processes and bottlenecks automatically.
Industry-Specific Automation Opportunities
Different industries are finding unique ways to leverage automation:
Healthcare: Automating patient scheduling, insurance verification, and medical record management while ensuring HIPAA compliance.
Financial Services: Streamlining loan processing, compliance reporting, and fraud detection while maintaining regulatory requirements.
Retail: Optimizing inventory management, order processing, and customer service to improve both efficiency and customer experience.
Manufacturing: Integrating production planning, quality control, and supply chain management for end-to-end operational excellence.
Preparing for Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation represents the future of business process optimization, combining RPA, BPA, AI, and other technologies into comprehensive automation ecosystems. This approach enables businesses to automate entire value chains rather than individual processes.
To prepare for hyperautomation, businesses should:
Develop automation governance frameworks
Invest in employee training and reskilling
Build integration capabilities between systems
Establish data quality and management practices
Create centers of excellence for automation initiatives
Conclusion: Finding the Right Automation Mix for Your Business
The choice between BPA and RPA isn't about picking a winner—it's about understanding which tool fits your specific business challenges and growth objectives. RPA delivers quick wins by automating individual tasks, while BPA provides strategic change by optimizing entire workflows. The most successful businesses use both technologies strategically, starting with high-impact RPA implementations and evolving toward comprehensive BPA solutions.
As we've explored throughout this guide, the automation landscape offers tremendous opportunities for small businesses willing to invest in the right technologies. The key is starting with a clear understanding of your current processes, realistic expectations about implementation timelines, and a commitment to proper change management.
The future belongs to businesses that can adapt quickly, serve customers efficiently, and scale operations without proportional increases in overhead. Automation technologies like BPA and RPA provide the foundation for this competitive advantage, but only when implemented thoughtfully and strategically.
Automation is not about replacing human workers—it's about empowering them to focus on high-value activities that drive business growth. By automating routine tasks and optimizing workflows, you free your team to innovate, build relationships, and solve complex problems that truly differentiate your business.
At WySmart.ai, we understand that small business owners need automation solutions that deliver results without overwhelming complexity. Our comprehensive, done-for-you AI toolbox combines the best of both RPA and BPA technologies, custom specifically for small business needs. We handle the technical complexity so you can focus on growing your business.
Ready to transform your business operations with intelligent automation? Boost your growth with a risk-free AI solution and find how the right automation mix can accelerate your success while reducing operational stress. Our money-back guarantee ensures you can explore automation benefits without financial risk.