
Why Banking Automation Has Become Essential for Modern Financial Institutions
Business process automation in banking industry is the use of technology to streamline and automate repetitive banking operations. The goal is to reduce manual work while improving efficiency, accuracy, and the customer experience.
Key Components of Banking Automation:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) - Software bots handling rule-based tasks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) - Smart decision-making and pattern recognition
Machine Learning (ML) - Predictive analytics and fraud detection
Digital Workflows - End-to-end process optimization
Integration Tools - Connecting legacy systems with modern platforms
The banking industry faces immense pressure to modernize. Manual processes that took days must now be completed in minutes to meet customer demands for instant services like account opening, loan decisions, and 24/7 support.
This shift is no longer optional. Banks that don't automate risk losing customers to agile fintech competitors. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this trend, making rapid digitization a necessity for survival.
The data is clear: McKinsey reports banks can cut operational costs by a third with process automation. Furthermore, 87% of organizations are adopting AI, and 94% of leaders see it as core to their operations.
Automation goes beyond cost-cutting; it's about enhancing customer and employee experiences while upholding strict banking compliance standards.
I'm Joey Martin, founder of WySMart.ai, and I've spent years helping businesses implement effective automation solutions. While my focus has been on small business automation, the principles of business process automation in banking industry mirror what I've seen transform countless operations—the key is starting with the right processes and scaling intelligently.
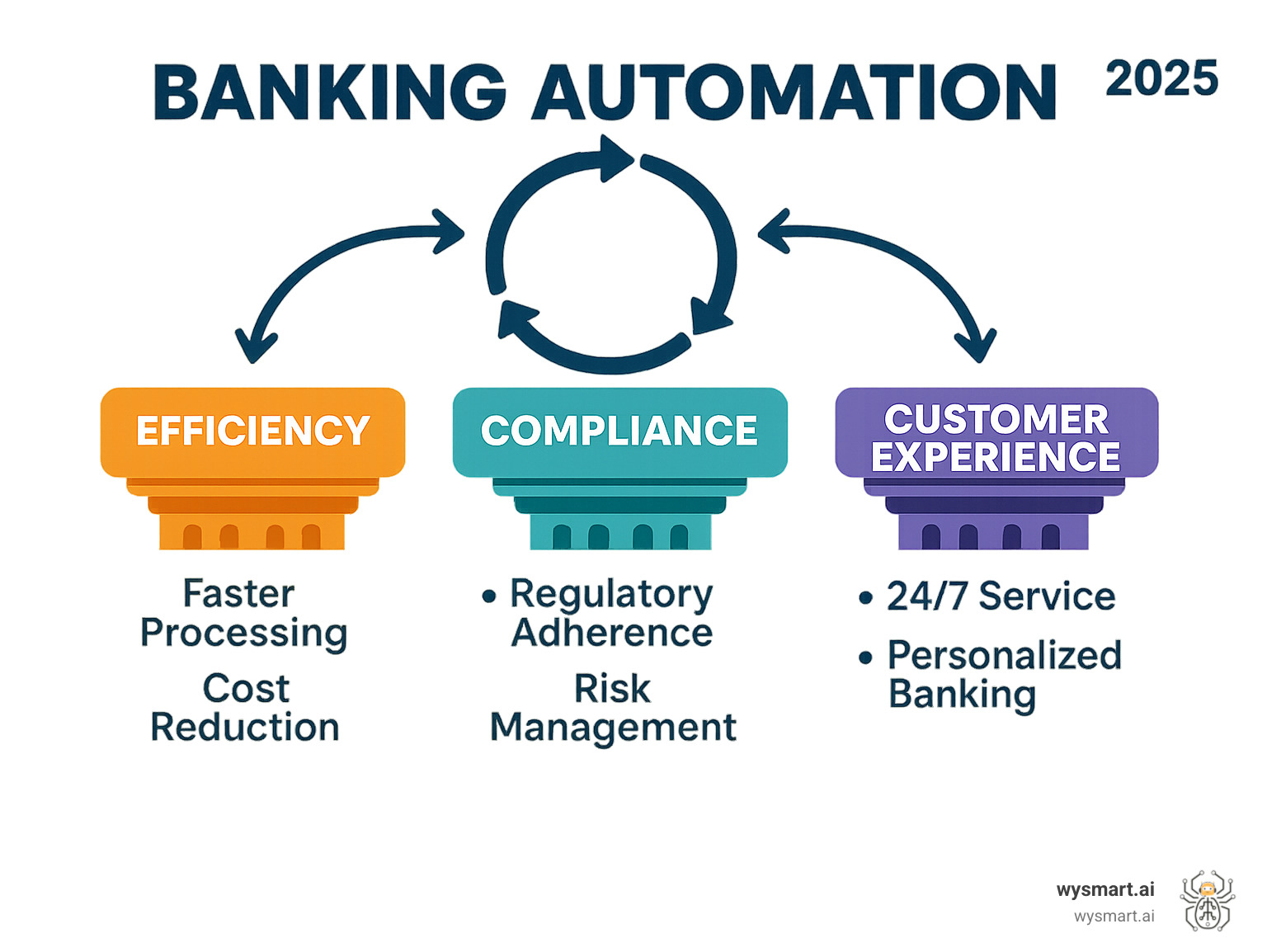
The Core Benefits of Automation in Banking Operations
Initially, banking automation sparked fears of job cuts for profit. However, the reality of business process automation in banking industry is more human-centered and transformative.

Automation revolutionizes all banking operations, not just by cutting costs, but by creating better experiences for both customers and employees. The transformative power of automation in banking manifests in three key areas: improved efficiency, solid compliance, and improved customer and employee experiences.
Driving Unprecedented Efficiency and Cost Savings
Automation's impact on efficiency is impressive, drastically reducing wait times for services like loan approvals. Faster processing times are a key benefit; banks have cut loan processing times by 50% using RPA for document verification, turning day-long processes into hours.
This speed boosts increased productivity, with companies reporting work processed 85 times faster with 90% fewer errors. The cost reduction is also significant. McKinsey finds banks can cut operational costs by a third through process automation, representing a fundamental change.
Automation also delivers scalability and 24/7 operations. Software bots work tirelessly, handling transaction spikes of 150% without overtime costs or employee stress.
Enhancing Compliance and Mitigating Risk
Banking regulations are complex and unforgiving, where a single compliance error can lead to millions in fines. Automation is a lifesaver for regulatory compliance, as systems ensure accuracy and timeliness. A European bank used RPA to improve its compliance reporting, eliminating last-minute scrambles.
KYC and AML processes are ideal for automation. They involve repetitive data checks against watchlists, a task where computers excel. In fact, 49% of business leaders report that AI's biggest impact is in KYC, AML, and fraud detection.
Automation also upgrades fraud detection. With 46% of organizations experiencing fraud, according to a PwC Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey, real-time analysis of transactions is crucial. Automated systems can spot suspicious patterns far faster than human analysts. Finally, they create detailed and consistent audit trails, providing regulators with comprehensive documentation on demand.
Revolutionizing the Customer and Employee Experience
From a human perspective, automation isn't about replacing people but improving their lives. Faster service delivery eliminates long waits for customers through instant account opening, quicker loan approvals, and real-time responses.
Automation enables personalized services by freeing up staff for complex customer needs. While 24/7 chatbots handle basic queries, they escalate complex issues to human agents. For employees, the change is dramatic. They can shift from tedious data entry and reconciliation to higher-value tasks that require their skills and creativity.
As a result, employee engagement improves. A Postbank case study showed automation boosted morale by allowing staff to focus on creative, valuable work. The result is a win-win: higher customer satisfaction from faster, personal service, and improved employee morale from more meaningful work. Notably, 53% of business leaders see AI's biggest impact in customer experience.
Key Use Cases for Business Process Automation in the Banking Industry
Today, business process automation in banking industry applications have expanded from simple data entry to sophisticated systems managing everything from customer onboarding to complex fraud detection.
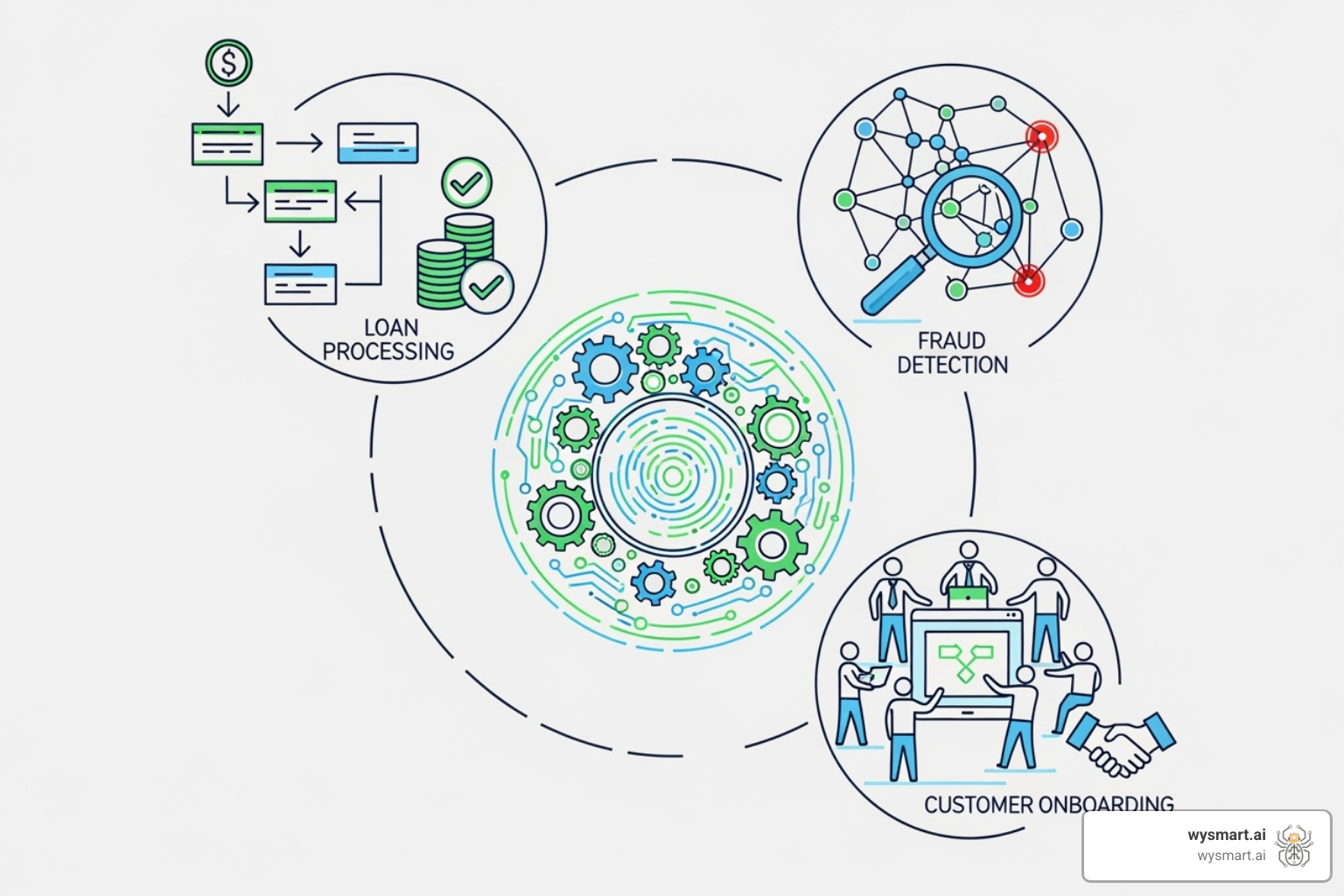
The versatility of banking automation is its strength, making a real difference in customer-facing processes, back-office operations, and critical security measures.
Common automated banking processes include: customer onboarding and account opening, loan processing and mortgage origination, KYC and AML checks, fraud detection and prevention, payments and settlements, customer service inquiries through chatbots, accounts payable and general ledger operations, regulatory reporting and compliance checks, data entry and reconciliation, and credit card processing.
Here are some of the most impactful ways banks use automation today.
Streamlining Customer-Facing Processes
Automated systems are changing experiences like opening a bank account, replacing hours of paperwork with a streamlined process. Customer onboarding is a prime example. Howard Bank reduced its paperless account opening time from 90 to 20 minutes, allowing staff to focus more on customers' financial goals. This is achieved through automated KYC checks that instantly verify customer data.
Loan processing automation offers another tangible customer benefit. Automated systems handle verification, scoring, and eligibility checks in a fraction of the time, with banks like ABC Bank cutting processing time by 50%. Similarly, mortgage origination is accelerated, as automation handles document collection, income verification, and credit reports, reducing the process from weeks to days.
For ongoing support, sophisticated chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 help with routine queries, freeing human agents to handle more complex issues.
Optimizing Back-Office and Internal Operations
Though invisible to customers, back-office operations are crucial for a bank's smooth functioning, and this is where automation delivers significant efficiency gains. Accounts payable and general ledger operations are ripe for automation. Grant Thornton, for instance, cut processing time by 60% using RPA bots to extract invoice data, match purchase orders, and process payments.
Automated report generation eliminates a tedious monthly task. For example, Zurich Insurance Group automated claims handling with machine learning and RPA, cutting manual data entry by 80%. In payment processing, one international bank reduced manual errors by 84% and boosted productivity by 70%. Back-office automation frees teams from repetitive work, allowing them to focus on strategic, creative problem-solving.
Automating Critical Compliance and Security Functions
Compliance is non-negotiable in banking. With strict regulations and severe penalties, manual processes can't handle modern requirements. KYC automation ensures rapid and accurate customer verification against watchlists, strengthening a bank's overall compliance posture.
In AML transaction monitoring, automation excels by analyzing vast transaction volumes in real-time to detect suspicious patterns indicative of money laundering. Sophisticated real-time fraud detection is also crucial, as 46% of organizations experience fraud. Machine learning algorithms instantly spot unusual activity and continuously improve their detection accuracy.
Automated compliance checks and data validation create comprehensive audit trails and ensure consistent adherence to regulations. A European bank found RPA improved not just the speed but the quality of its compliance reporting.
From RPA to AI: The Technologies Powering Banking Automation
The evolution of business process automation in banking industry is like the jump from calculators to smartphones. It has progressed from basic software robots for repetitive tasks to intelligent systems capable of learning and complex decision-making.
This journey is powered by key technologies: Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the emerging fields of Agentic AI and Hyperautomation. Together, they are changing banking operations.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA can be thought of as a tireless, error-free digital worker. These software robots mimic human actions to interact with computer systems 24/7. RPA excels at rule-based, repetitive processes like data entry, form filling, and data migration. It is especially valuable for its ability to integrate with legacy systems, acting as a bridge to modern technology without costly overhauls. RPA's simplicity allows for quick implementation, but its main limitation is that it can only follow pre-programmed rules.
The Rise of Intelligent Automation: Integrating AI and Machine Learning
Intelligent automation combines RPA's "doing" with the "thinking" of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). This creates systems capable of decision-making and learning from experience. Unlike RPA, AI processes unstructured data like emails and complex documents. Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables systems to understand human language, improving tools like chatbots.
Machine Learning enables pattern recognition and predictive analytics, helping banks identify potential loan customers or suspicious transactions. These systems improve over time by learning from new data. The commitment is clear: 87% of organizations are rolling out AI, and 94% of leaders consider it core to their operations.
The Future is Agentic: Exploring Agentic AI and Hyperautomation
Agentic AI represents the next frontier: autonomous agents that manage dynamic workflows and work towards goals without constant human supervision. For example, an AI agent processing a loan could gather information, assess risk, and negotiate terms, learning from each case to improve its performance.
Hyperautomation is a strategy for end-to-end process automation, combining technologies like RPA for tasks, AI for decisions, and ML for continuous improvement. This is a paradigm shift in how banks operate, moving toward a future where intelligent systems handle complex tasks, freeing humans for strategic and creative work. Banks are evolving from transaction processors to intelligent organizations that anticipate customer needs. The goal is not just speed, but intelligence.
A Strategic Roadmap for Successful Automation Implementation
Starting on business process automation in banking industry requires a strategic approach, not just technology selection. Rushing without a plan often leads to avoidable setbacks. Successful implementation is a change management challenge that requires orchestrating people, processes, and technology to achieve lasting results.

At WySmart.ai, we've seen that successful projects begin with a clear strategy, use pilot projects for quick wins, and establish strong governance for long-term success.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Implementing banking automation has common challenges. Recognizing them upfront can prevent significant frustration and delays.
Legacy system integration is a major hurdle. Banks' decades-old IT infrastructures weren't designed for modern tools, making integration complex.
Data security concerns are paramount. Any automated process must have top-tier cybersecurity, encryption, access controls, and regulatory compliance.
The high initial investment can be a barrier. Despite a strong long-term ROI, securing approval for upfront costs requires clear financial projections.
Employee resistance is a significant human challenge. Fear of job loss can lead to reluctance to adopt new processes.
The skills gap is a real challenge. Banks need specialized expertise in RPA, AI, and data science, requiring them to either upskill their current workforce or recruit new talent.
Best Practices for a Smooth Transition to Business Process Automation in the Banking Industry
Based on experience, six critical practices distinguish successful automation implementations.
Start small with pilot projects. Don't automate everything at once. Identify a high-impact, rule-based process to start. This demonstrates value, provides learning opportunities, and builds confidence for scaling.
Define clear KPIs before you begin. Set specific, measurable goals, such as reducing processing time by 50% or cutting costs by 30%. These metrics provide focus and concrete evidence of success.
Ensure stakeholder buy-in by engaging all affected departments from the start. Input from IT, operations, compliance, and front-line staff is essential for smooth adoption.
Provide comprehensive employee training. Go beyond tool usage to explain how automation improves roles, not replaces them. Show how it frees them for strategic work. When employees see automation as an ally, adoption is smoother.
Choose scalable solutions that can grow with your bank. Select platforms with strong integration, low-code options, and the ability to handle increasing complexity.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement. Automation is not a one-time fix. Regularly analyze performance, gather feedback, and refine workflows to ensure your business process automation in banking industry efforts deliver maximum value.
Frequently Asked Questions about Banking Automation
Across industries, banking automation raises common questions. Here are some insights on how business process automation in banking industry works in practice.
What is the difference between BPA and RPA in banking?
Understanding the distinction helps in making better automation decisions.
Business Process Automation (BPA) is the high-level strategy. It's about redesigning and optimizing entire end-to-end workflows across the organization to improve overall efficiency.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology used to execute specific tasks. It uses software robots to handle repetitive, rule-based activities like data entry or generating reports.
In practice, a bank might use BPA to redesign its entire loan application process. Within that new workflow, it would use RPA to automate specific tasks like extracting data from forms. The key difference is scope: RPA is for task automation, while BPA is for process optimization. Successful projects typically use RPA as a tool within a broader BPA strategy.
How does automation affect jobs in the banking sector?
This is a common concern. My observation is that automation leads to task augmentation, not job elimination. Like calculators for accountants, it removes tedious work, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities like analysis and strategy.
Automation takes over mundane, repetitive work like data entry, freeing employees for higher-value tasks that require human skills like problem-solving, customer relationship building, and strategic thinking. The Postbank case study confirms this: automating repetitive tasks improved employee morale significantly, as staff could focus on more creative and valuable work.
This causes a shift to more strategic roles, creating a need for reskilling. The outcome is reduced mundane work, an improved employee experience, and new opportunities for career growth.
Is business process automation in the banking industry only for large banks?
Not at all. This is a common myth. With scalable solutions and cloud-based tools, automation is now accessible without a massive IT department or budget.
Low-code platforms are game-changers, enabling business users, not just developers, to create automated workflows. This levels the playing field for smaller banks. Cloud-based tools also remove the need for expensive on-premise infrastructure, making powerful automation accessible to credit unions and community banks through a subscription model.
The key for smaller banks is to start smart by targeting specific, high-impact pain points first. Small institutions often see dramatic results by focusing on one or two processes initially. The benefits for community banks can be even greater due to their more manual starting point.
The bottom line is that business process automation in banking industry is for institutions of all sizes. The tools are affordable, accessible, and scalable.
Conclusion
The banking world is changing rapidly, and business process automation in banking industry is a driving force. Automation is no longer a nice-to-have; it's essential for any bank that wants to thrive.
As we've covered, banks are cutting costs, improving customer experiences, and shortening loan processes from weeks to hours. Employees are shifting from spreadsheets to building customer relationships. This is transformative change.
The technological journey from RPA to AI is remarkable. We've moved from basic task bots to intelligent systems, and are now entering an era of agentic AI and hyperautomation that promises autonomous banking operations.
While the road to automation has challenges like legacy systems and security concerns, successful banks of all sizes share a common strategy: start small, set clear goals, and involve your people.
What really excites me about the future of banking is how automation is making financial services more human. By handling repetitive tasks, it frees people to focus on what they do best: problem-solving, relationship-building, and innovation. That's a win for everyone.
For any financial institution still sitting on the fence, the competitive advantage is clear. Automation meets customer demands for speed, regulatory needs for compliance, and business needs for efficiency. Business process automation in banking industry delivers on all three fronts.
At WySmart.ai, we've seen how the right automation strategy can transform businesses across industries. While we specialize in helping small businesses open up the power of AI and automation, the principles we've discussed here apply universally. It's about creating systems that work smarter, not harder.
The future of banking is digital, intelligent, and surprisingly human. The question isn't whether to accept automation - it's how quickly you can get started. Visit us at https://wysmart.ai to find how we can help transform your operations with our comprehensive, done-for-you AI solutions.