
Automation Explained: Your Guide to How BPA Gets Things Done
Why Business Process Automation Is Changing How Work Gets Done
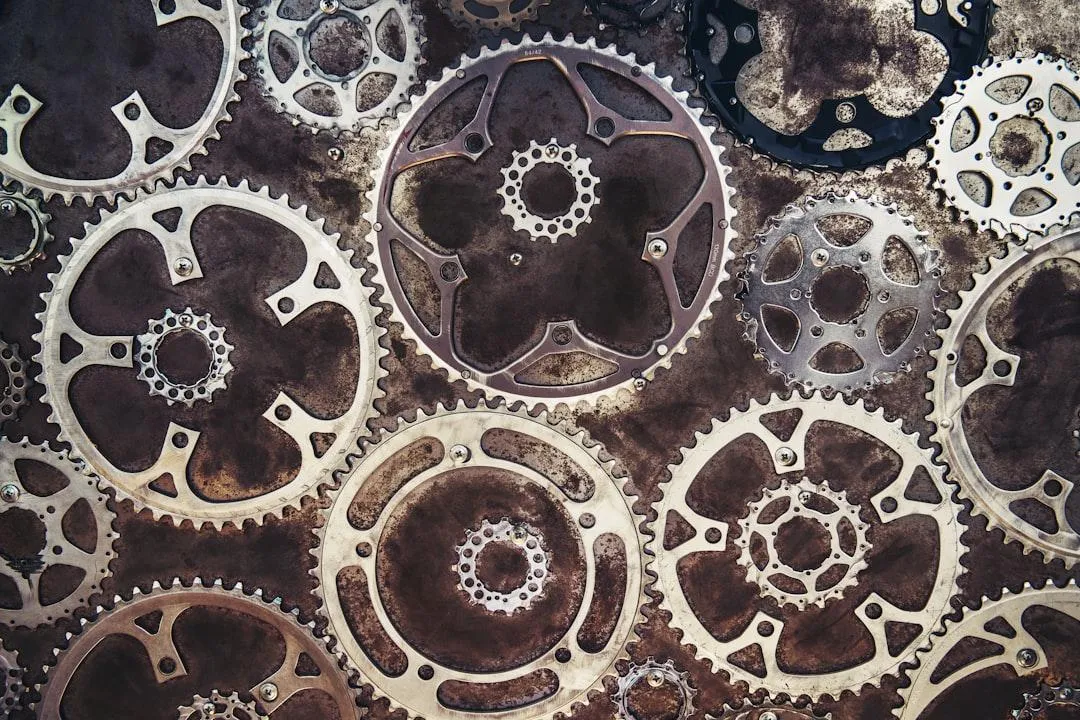
How does business process automation work? Business process automation uses software to automatically handle repetitive business tasks. It works by creating digital workflows that connect different systems, trigger actions based on specific conditions, and move information between departments without human intervention.
Here's the basic process:
Identify the process - Map out manual tasks that follow consistent rules
Design the workflow - Create digital steps that mirror the manual process
Set up triggers - Define what starts the automated process (like receiving an email or form submission)
Connect systems - Link different software tools so data flows automatically between them
Test and deploy - Run the automation to ensure it works correctly before going live
Monitor and improve - Track performance and make adjustments as needed
This massive data explosion makes manual processes inefficient and error-prone. In fact, data errors cost U.S. businesses $3 trillion annually, making automation essential for staying competitive.
Around 60% of companies already use automation tools in their workflows, and the automation market is projected to reach $23.9 billion by 2029. For small businesses, this represents an opportunity to level the playing field with larger competitors.
I'm Joey Martin, founder of WySmart.ai. I've spent years helping small business owners use business process automation to transform their operations. I've seen how the right automation strategy frees up time and resources while improving customer experiences.
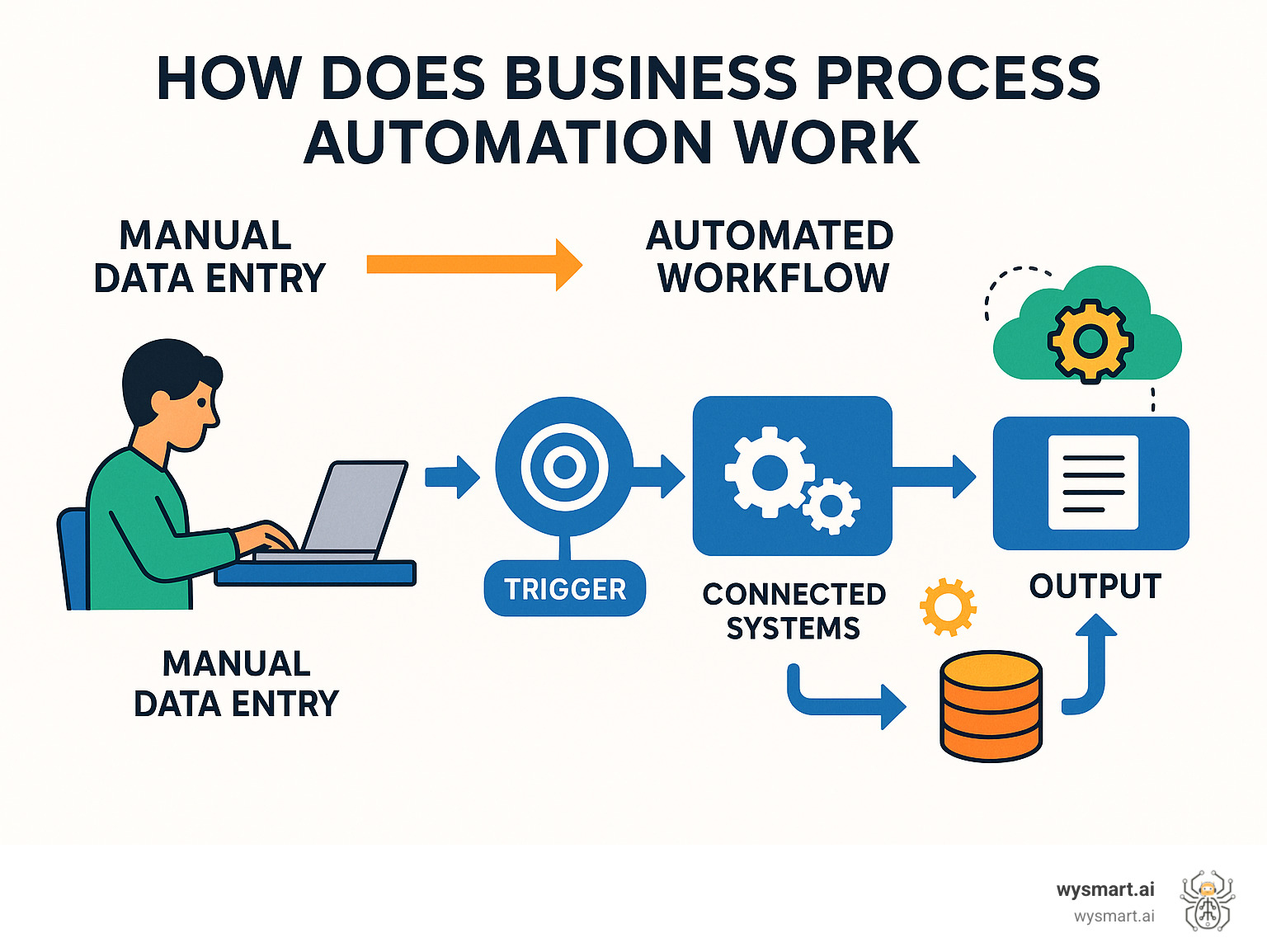
What is Business Process Automation (and Why Does It Matter)?
Business Process Automation (BPA) is a strategic approach that uses technology to handle repetitive, time-consuming tasks. Instead of manually processing invoices or copying data, you set up digital workflows to do the heavy lifting. BPA is about streamlining entire operations across departments. For example, a single customer order can trigger automated inventory updates, confirmation emails, shipping label creation, and accounting notifications.
The Core Goal: More Than Just Speed
While speed is a benefit, the core goal of BPA is to free up your employees for more valuable work, like creative problem-solving and building customer relationships. This allows your team to focus on strategic work that grows the business, like sales prospecting or handling complex customer issues.
Improving quality is another key benefit. Automated processes reduce human error, leading to fewer mistakes and greater consistency. Ensuring compliance is also simplified, as automated systems create a complete, auditable record of every transaction. These improvements lead to improved customer satisfaction through faster, more accurate service.
BPA vs. RPA vs. BPM: Clearing Up the Confusion
It's easy to get confused by automation acronyms. Here's a quick breakdown of BPA, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and Business Process Management (BPM):
Feature Business Process Automation (BPA) Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Business Process Management (BPM) Scope Automates entire business processes across multiple departments and systems Automates specific repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions A management approach for analyzing and optimizing all business processes Purpose Streamline complete workflows, reduce errors, improve efficiency across the organization Handle high-volume, rule-based tasks like data entry or form processing Continuously improve how business processes work before automation Implementation Deep system integration with custom workflows and strategic planning Software "bots" that interact with existing applications like a human would Process mapping and analysis to identify improvement opportunities
In short, BPA is a holistic strategy for end-to-end process change. RPA focuses on automating specific, repetitive tasks, while BPM is a management discipline for analyzing and optimizing processes before automation. Understanding how does business process automation work starts with recognizing that it's the comprehensive approach that delivers the biggest impact.
So, How Does Business Process Automation Work?
So, how does business process automation work in practice? It relies on software platforms and workflow engines to design, execute, and manage automated processes.

Modern workflow designer tools provide a digital canvas with drag-and-drop elements, allowing you to visually map out every step of a process. These systems use triggers—specific events like a form submission or a new email—to initiate a pre-defined sequence of automated actions.
The real power comes from system integration via APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which allow data to flow automatically between your CRM, accounting software, and other tools without manual data entry. Many platforms also offer pre-built templates for common processes, making it easier to get started. This accessibility is why around 60% of companies already use automation tools in their workflows.
The Core Mechanics: How Does Business Process Automation Work Step-by-Step?
Implementing BPA follows a clear, step-by-step process:
Step 1: Identify & Analyze the Process. Find repetitive, time-consuming tasks and map out the current process to identify bottlenecks. Don't automate a broken process.
Step 2: Map the Workflow. Use a visual designer to create a blueprint of the new, automated process, outlining every step and decision point.
Step 3: Define Rules & Logic. Set up the "if-then" conditions that guide the automation. For example, if a purchase request is over $500, route it to a manager for approval.
Step 4: Integrate Systems & Data. Use APIs to connect your different software applications, ensuring data flows seamlessly between them.
Step 5: Test & Deploy. Thoroughly test the automation with various scenarios to ensure it works correctly before rolling it out, often starting with a small pilot group.
Step 6: Monitor & Optimize. Continuously track performance metrics like processing time and error rates to find opportunities for further improvement.
The Technology Behind BPA
Workflow orchestration is the core technology that manages the sequence of automated tasks and human activities, ensuring they work together seamlessly.
Low-code and no-code platforms have made BPA accessible to non-technical users. They allow you to build powerful automations using visual interfaces and drag-and-drop tools instead of complex code.
AI-driven automation adds intelligence to processes. AI can interpret unstructured data like emails, while Machine Learning (ML) allows the system to learn and improve over time.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the connectors that allow different software to share data. They are essential for creating a unified, automated system where information flows instantly between your tools.
Putting BPA to Work: Common Processes and Real-World Examples
Business process automation can transform operations in every department. In practice, how does business process automation work? It replaces repetitive, rule-based tasks with smart, automated workflows.
Tasks like data entry, routing approvals, and sending status updates are prime candidates for automation. The goal is to improve operational efficiency so your team can focus on higher-value work.
Human Resources (HR)
HR departments are often burdened with administrative tasks. Employee onboarding is a prime example where automation can orchestrate the entire process: triggering background checks, sending welcome materials, and setting up software access. This creates a smooth experience for new hires and frees up HR staff. Other key HR automations include seamless leave requests, error-free payroll processing, and streamlined performance reviews. For more insights, explore HR automation best practices.
Finance and Accounts Payable
Accuracy is critical in finance, making it a key area for automation. Invoice processing can be fully automated, from receiving and categorizing invoices to routing them for approval. This reduces errors and speeds up payments. Similarly, purchase order approvals, expense reporting, and financial report generation can be automated to save time and ensure policy compliance. To dive deeper, consider accounts payable automation insights.
Sales and Marketing
For sales and marketing teams, automation enables speed and personalization at scale. Automated lead nurturing can trigger personalized email sequences based on prospect behavior. Automating CRM data entry ensures all teams have access to accurate, up-to-date customer information. Other impactful automations include automated lead scoring, personalized email campaigns, follow-ups for abandoned carts, demo scheduling, pipeline updates, quote generation, brand mention monitoring, and content distribution.
Customer Service
In customer service, automation improves response times and consistency. Ticket routing automatically directs inquiries to the right person based on keywords or urgency. Automated responses and chatbots can handle FAQs 24/7, and knowledge base updates can be automated to build a self-service resource for customers. For more examples, explore customer service automation examples.
Successful BPA starts with automating clearly defined, repetitive, rule-based processes.
Your Roadmap to Successful BPA Implementation
Implementing Business Process Automation requires strategic planning, a phased approach, and solid change management. It's a fundamental change to how your business operates, so every step must be thoughtful.
With the automation market projected to reach $23.9 billion by 2029, it's clear that businesses are seeing real value. Measuring ROI is at the heart of any successful implementation. Track clear metrics against your goals, whether it's cost savings or efficiency gains. The smartest approach is to start small, learn, and scale up gradually.
Key Steps to Get Started
Your BPA journey can be broken down into these manageable steps:
Define clear goals. Know what you want to achieve, such as cutting error rates or speeding up processing.
Start small. Pick one or two high-impact, repetitive processes to secure an early win and build momentum.
Involve stakeholders. Get input from the employees who perform the tasks daily. Their insights are crucial for designing effective workflows and ensuring buy-in.
Document everything. Create a blueprint of your current and future processes to help identify rules, train your team, and simplify troubleshooting.
Train your team. Provide thorough training and support. Help your team understand how automation will improve their work by freeing them from tedious tasks.
Choosing the Right Tools: How Does Business Process Automation Work in Practice?
Choosing the right BPA tool can be daunting. Focus on your actual needs, not just flashy features.

Look for these key features: intuitive workflow management, insightful process monitoring, clear reporting, and robust exception handling. Also consider:
Integration capabilities: Your tool must connect with your existing systems like CRM and accounting software.
Scalability: Choose a platform that can grow with your business.
Security: Ensure the platform has strong encryption and robust access controls.
Analytics and reporting: Dashboards should help you monitor performance and measure ROI.
User-friendliness: Low-code/no-code interfaces empower your team to build and modify workflows without relying on IT.
For comprehensive guidance, consider downloading The Process Automation Buyer's Guide.
Overcoming Common Challenges
BPA implementation has its challenges, but being prepared helps you overcome them.
High initial costs: View the upfront investment as a path to long-term ROI through increased efficiency and fewer errors.
Employee resistance: Address concerns with open communication. Explain that BPA is meant to improve their roles by eliminating tedious tasks, not to replace them.
Lack of technical expertise: Low-code tools help, but complex integrations may require specialized knowledge. Invest in training or partner with experts.
Over-automating: Don't automate a messy process. Analyze and streamline your workflows first to avoid creating an automated mess.
Data quality issues: Poor data leads to poor automation results. Clean your data and establish governance policies before you begin.
Frequently Asked Questions about Business Process Automation
When learning how does business process automation work, several common questions arise. Here are straightforward answers to the most frequent ones.
What is the difference between workflow automation and business process automation?
These terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Workflow automation focuses on a specific sequence of tasks for a single process, like a vacation request approval. It's typically contained within one department.
Business process automation (BPA) is broader and more strategic. It orchestrates multiple workflows and systems across different departments to automate an end-to-end process, like order fulfillment, which involves sales, inventory, shipping, and accounting.
Can small businesses really benefit from BPA?
Absolutely. Small businesses often benefit even more from BPA than large enterprises. While large companies have used automation for years, modern low-code tools have made it accessible and affordable for everyone.
For small businesses where every team member wears multiple hats, automating repetitive tasks frees up critical time for growth activities like customer engagement and product development. Automation allows small businesses to compete with larger companies by improving efficiency and delivering professional, responsive service without a large staff.
Does business process automation eliminate jobs?
This is a common concern, but the reality is positive. The primary goal of BPA is not to eliminate jobs but to eliminate the mundane, repetitive parts of jobs that people dislike, such as manual data entry.
By automating these tasks, we free employees to focus on more fulfilling and valuable work, like improving customer relationships or strategic planning. Automation transforms jobs, it doesn't eliminate them. An employee's role might shift from manual processing to overseeing and optimizing the new automated system. This shift empowers your team to use their unique human skills—creativity, problem-solving, and judgment—while technology handles the rest.
Conclusion
As we've seen, understanding how does business process automation work reveals a fundamental shift in how modern businesses operate. BPA is not a passing trend but a strategic necessity.
We've covered the mechanics of BPA, from identifying processes to deploying workflows. We've seen its impact in HR, finance, and customer service, and outlined the steps for successful implementation and tool selection. The data is clear: automation is essential for staying competitive. More importantly, it's about empowering our employees.
By removing repetitive tasks, we free our teams to focus on innovation, creativity, and building meaningful customer relationships—the work that drives real growth. BPA drives efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures compliance. It builds more agile, resilient, and human-centric businesses.
For small businesses, this is a massive opportunity. Accessible tools now level the playing field, allowing you to compete with larger companies while retaining your unique personal touch.
For small businesses looking to leverage the power of AI-driven automation for marketing, sales, and operations, WySmart.ai offers a comprehensive, done-for-you solution, designed to boost growth and reduce stress without the overwhelm of figuring it all out yourself.
Ready to see how automation can transform your business? Explore how to get started with automation and find what's possible when technology works for you, not against you.